Table of Contents
Photosynthesis Definition
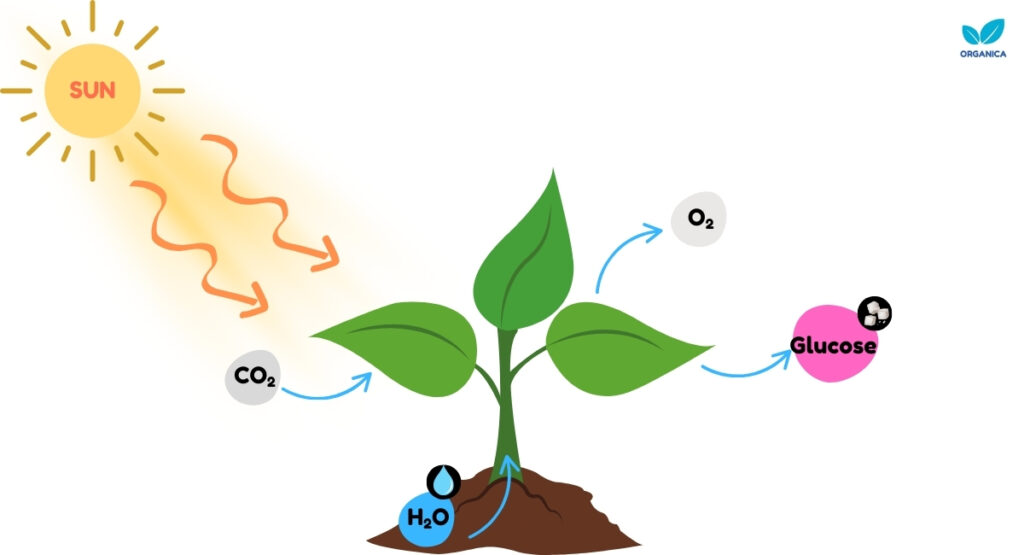
What is photosynthesis? Photosynthesis is a very important process that occurs in plants. It involves the making of food (glucose) from raw materials using energy from sunlight.
Plants are autotrophs, meaning that they make their food. Their green leaves capture sunlight energy and use it to turn water and carbon dioxide into glucose and oxygen. Animals on the other hand, rely on the food that plants produce.
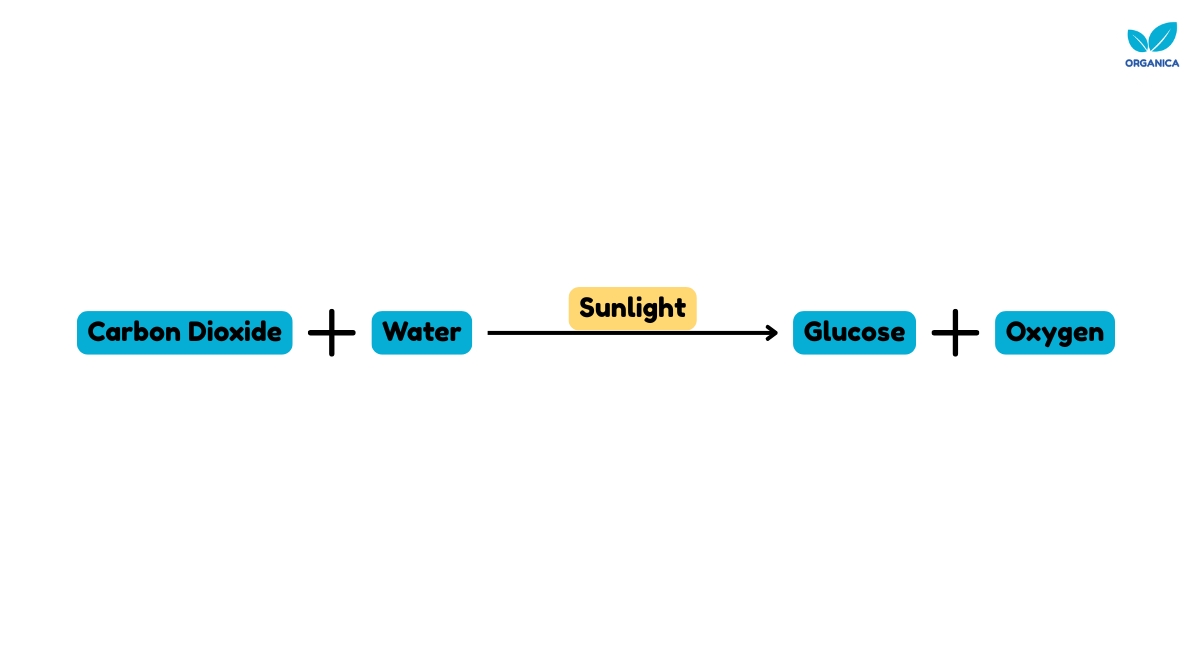
Chemical Equation
The carbon dioxide and water that plants use to make their food are called “reactants”. A reactant is any substance or molecule that undergoes a chemical change during a reaction. In the presence of sunlight, plants use carbon dioxide and water in photosynthesis to produce glucose and oxygen.
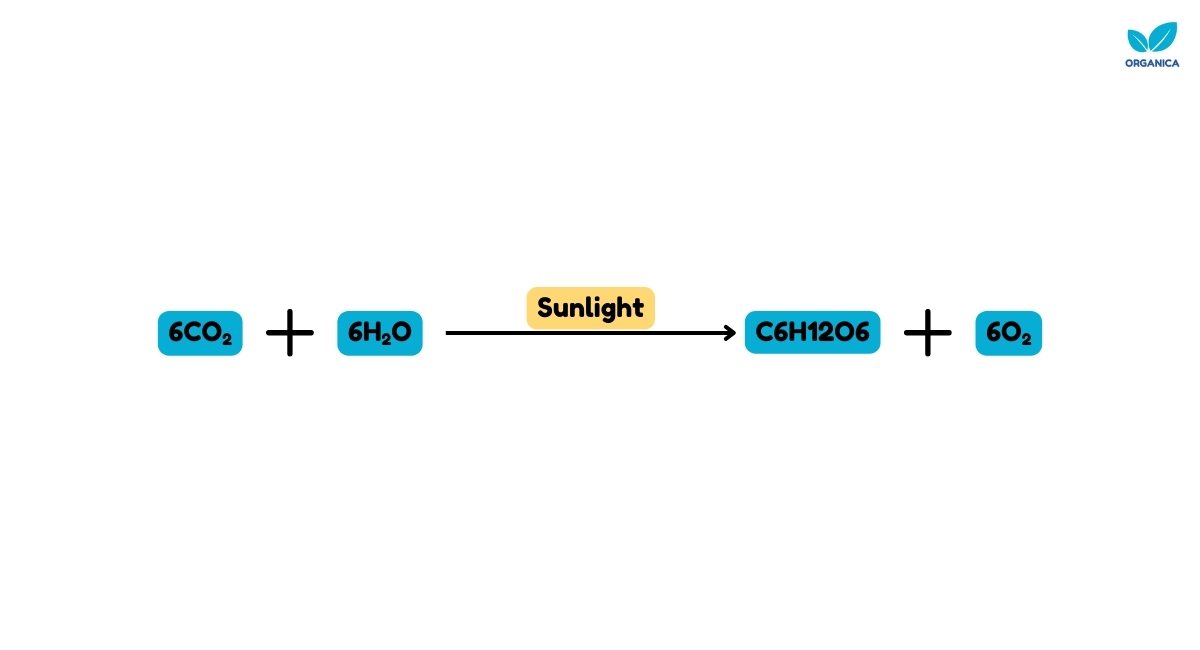
Up to this point, you might have assumed that one molecule of carbon dioxide is used to produce a molecule of glucose, which is not true. In fact, six molecules of carbon dioxide are used to produce one glucose molecule because glucose is a six-carbon molecule.
Chlorophyll
Imagine you’re shining a flashlight onto a bucket of water put in a carbon dioxide enclosure. What do you think will happen? Glucose will not be produced because plant leaves use chlorophyll to carry out photosynthesis.
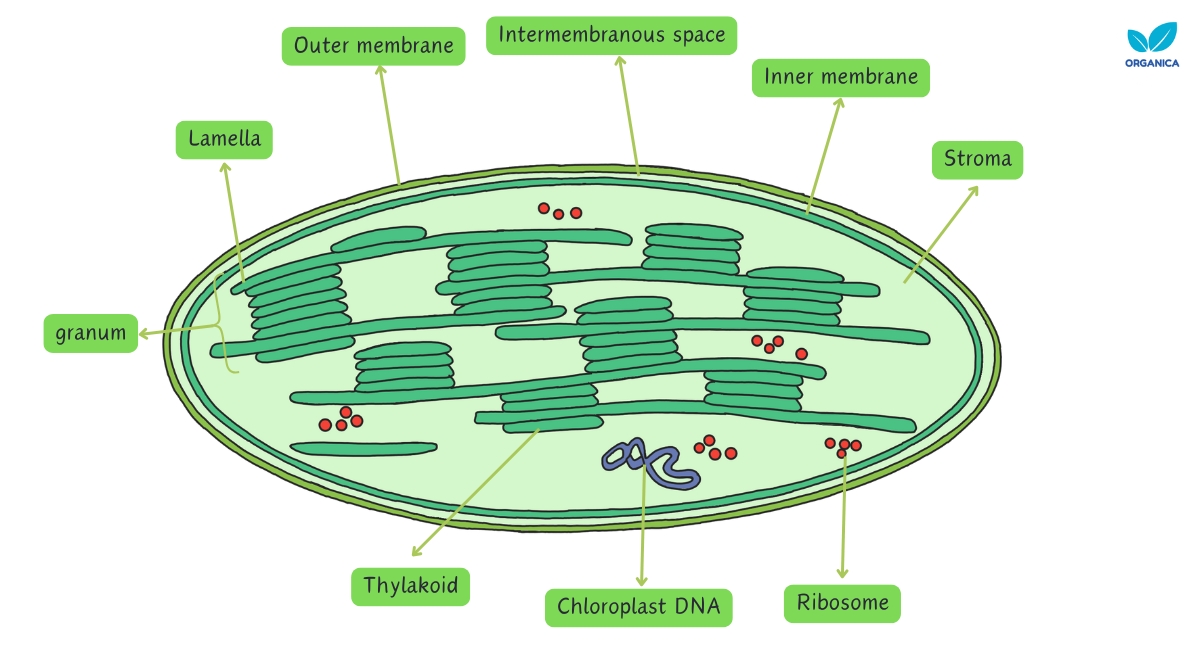
Chlorophyll is a specialised molecule that absorbs light energy from the sun. This captured energy is then used to power photosynthesis, helping plants make glucose from carbon dioxide and water.
It is a green pigment located in the chloroplast of the plant cell and algae.
Importance
Glucose produced through photosynthesis is used for many different purposes:
–Release of useful energy (ATP)
Chemical bonds in glucose store energy that can be used for various activities. For example, energy in the form of ATP is needed for the transport of minerals and water molecules between root hair cells.
–Stored as starch
If a lot of glucose is produced, plants store it in the form of starch. Starch is a polysaccharide made by linking glucose molecules together. Plants store it in their roots, seeds, and tubers as an energy reserve. Starch molecules do not get involved in chemical reactions because they are insoluble in water.
–Sucrose for transport
Glucose can be made in specific parts of the plant. Other parts have glucose delivered to them in the form of sucrose. It is made of one glucose molecule and another similar molecule (fructose) linked together. Plants transport it as a soluble form of energy, and humans use it as table sugar.
– Cellulose for plant cell walls
Cellulose is a polysaccharide composed of long chains of glucose. It is the main structural component of the cell wall, giving strength and support.
Factors affecting photosynthesis
Carbon Dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a crucial component of photosynthesis. If the concentration of carbon dioxide is low, photosynthesis occurs at a slower rate.
Water
Like carbon dioxide, a shortage of water can significantly reduce the rate of photosynthesis
Light intensity
Light intensity controls how much energy is available. It acts as the “catalyst” since it powers photosynthesis; too little slows it down, but too much can cause saturation.
Photosynthesis and Cellular Respiration
The relationship between photosynthesis and cellular respiration forms the fundamental block for life as we know it today. The products of one reaction are the reactants of the other. In this case, water and carbon dioxide are used in photosynthesis to produce glucose and oxygen, and vice versa.
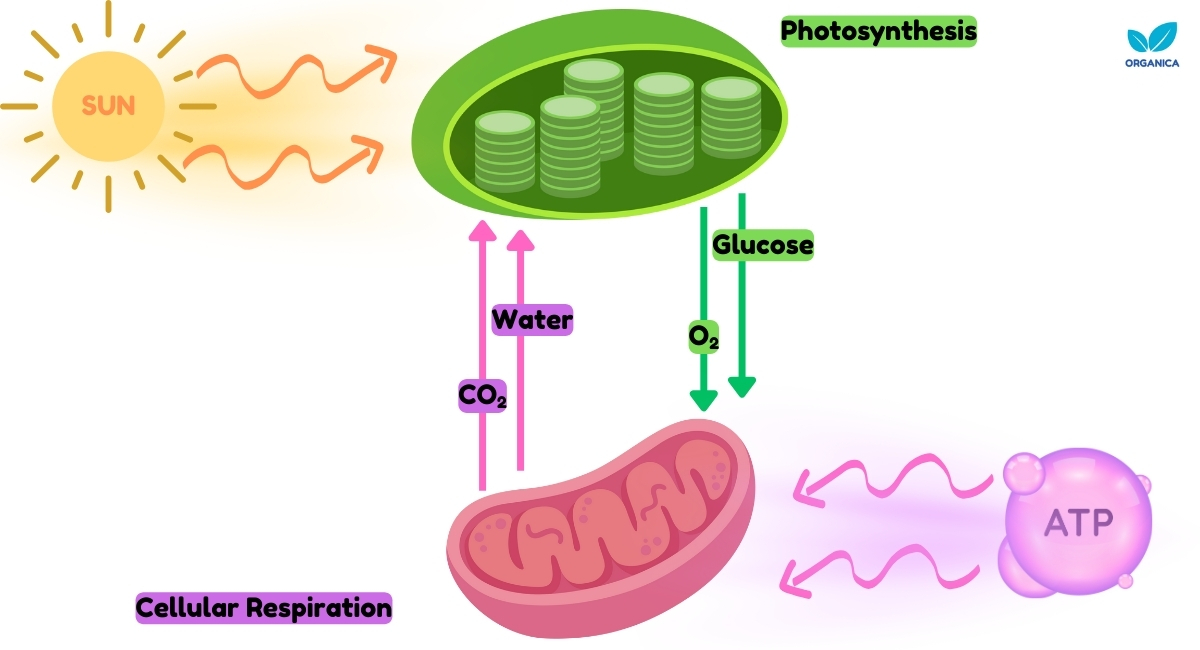
Cellular respiration utilises the products of photosynthesis to produce energy for animals to live and survive. Without photosynthesis, cellular respiration can not occur, and oxygen-dependent organisms will go extinct.
